Define Catalyst In Biology . Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Web a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. Web in chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Web thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence.
from www.slideserve.com
Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Web in chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. Web a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Web thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence.
PPT Enzyme and Catalysis PowerPoint Presentation, free
Define Catalyst In Biology Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Web thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence. Web a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. Web in chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction.
From www.slideserve.com
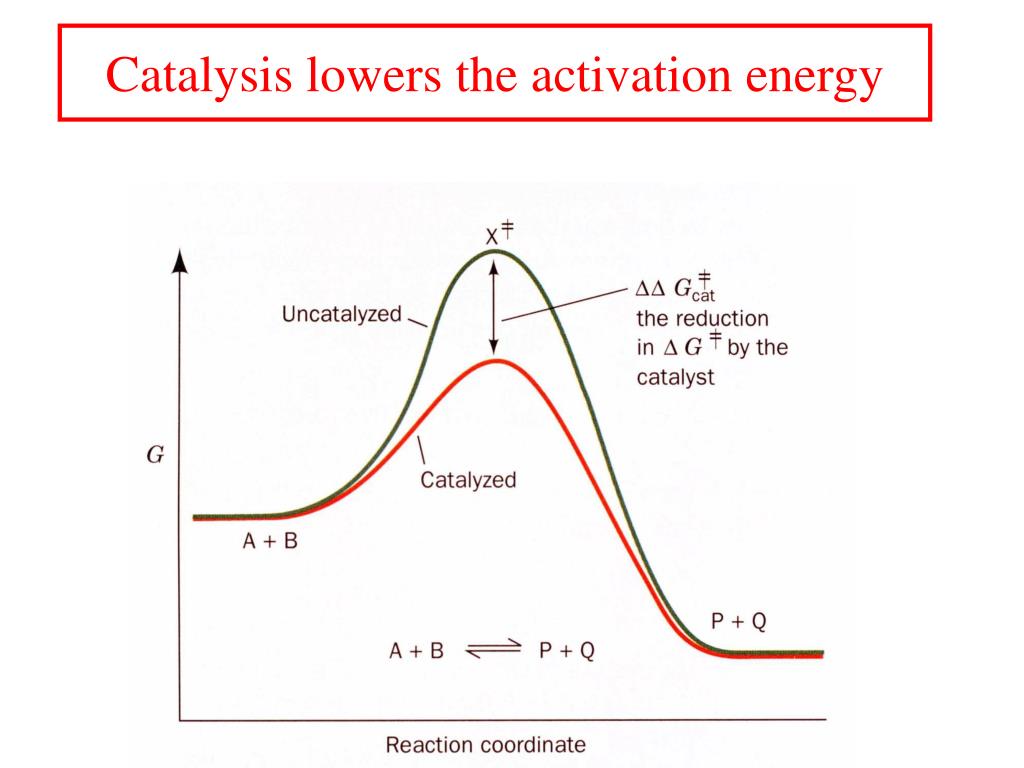
PPT CATALYSIS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID270211 Define Catalyst In Biology Web in chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed.. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Catalysts PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2684800 Define Catalyst In Biology Web a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 2Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5566824 Define Catalyst In Biology Web in chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Web describe the role of. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From study.com
Catalyst Definition, Types & Function Lesson Define Catalyst In Biology Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Web in chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. Web thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Catalyst Examples For Kids Define Catalyst In Biology An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. Web in chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.expii.com
Catalysts (Enzymes) — Overview & Examples Expii Define Catalyst In Biology Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Web a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web describe the role of enzymes. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Factors that Affect Rate of Reaction PowerPoint Presentation Define Catalyst In Biology Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From bio1151.nicerweb.com
catalytic.html 08_17CatalyticCycle.jpg Define Catalyst In Biology An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. Web a substance that. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.scribd.com
Biological Catalysts (13) Hydrolysis Enzyme Define Catalyst In Biology Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.nagwa.com
Lesson Catalysts Nagwa Define Catalyst In Biology Web a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. Web catalyst, in chemistry,. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From danieljcunninghamxo.blob.core.windows.net
How Are Enzymes Act As Biological Catalysts Define Catalyst In Biology Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. Web in chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. Web a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.researchgate.net
1 Schematic illustration of a catalytic process showing "A" and "B Define Catalyst In Biology Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Web thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence. Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From slideplayer.com
Biological catalysts Enzymes IGCSE Biology. ppt download Define Catalyst In Biology An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction. Web thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Web a substance that. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT ENZYME PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1344148 Define Catalyst In Biology Web thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From gamesmartz.com
Catalyst Definition & Image GameSmartz Define Catalyst In Biology Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. Web in chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the rate of a chemical reaction without. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.thoughtco.com
Catalysis Definition in Chemistry Define Catalyst In Biology Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzymes Organic Catalysts PowerPoint Presentation, free download Define Catalyst In Biology Web thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence. Web a catalyst is a something that helps increase the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. An. Define Catalyst In Biology.
From www.mdpi.com
Catalysts Free FullText General and Prospective Views on Oxidation Define Catalyst In Biology Web in chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. Web catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Web thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in. Define Catalyst In Biology.